In genetics, a deletion (also called gene deletion, deficiency, or deletion mutation ) (sign: Δ) is a mutation (a genetic aberration) in which a part of a chromosome or a sequence of DNA is left out during DNA replication. Any number of nucleotides can be delete from a single base to an entire piece of chromosome. This uncopied part can be as small as a single nucleotide or as much as an entire chromosome.
Mistakes during DNA replication can happen, and one of the most common mistakes in this process is called a deletion mutation. However, before we can get into the specifics of this type of mutation, it is important to take a brief look at the basic process of DNA replication in the nucleus of cells. MUTATION in which genetic material is removed from chromosomes or other DNA molecules (see CHROMOSOMAL MUTATION, POINT MUTATION). A nonsense mutation is also a change in one DNA base pair.
Instead of substituting one amino acid for another, however, the altered DNA sequence prematurely signals the cell to stop building a protein. This type of mutationin a shortened protein that may function improperly or not at all.
Different types of indel mutation. Panel C is simply a deletion and not a frameshift mutation.

A frameshift mutation (also called a framing error or a reading frame shift) is a genetic mutation caused by indels (insertions or deletions) of a number of nucleotides in a DNA sequence that is not divisible by three. Example of Deletion Mutation : 22q11. This disease is characterized by cleft palate, heart defects, autoimmune disorders etc.
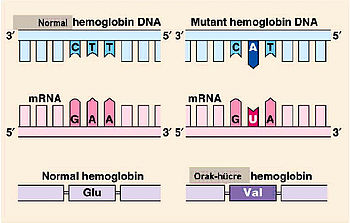
Kromozom Mutasyonları Kromozom mutasyonları, kromozomun bir parçasında kopma veya parça değişimi ( crossing-over) sırasında yanlış yapısal ya da sayısal değişiklikler sonucu oluşur. The deletion occurs near the middle of the chromosome at a location designated q11. A small-scale type of deletion mutation is one in which one or more nucleotide s are lost or deleted from the chromosome (microdeletions).
Deletion mutations that occur towards the ends of a chromosome are referred to as terminal deletions. What is a deletion mutation ? The dystrophin gene is the biggest in human cells – the DNA code is more than 10letters long and deletions can range in size from just a few letters to many thousands of letters.
A deletion occurs when more than one letter is deleted from the DNA code. Deletion is a type of mutation involving the loss of genetic material.
It can be small, involving a single missing DNA base pair, or large, involving a piece of a chromosome. Again, this causes the entire reading frame to change. It alters the codon and will also affect all amino acids that are coded for after the deletion.
Schematic diagram of the primer design for site-directed mutagenesis. Deletions are mutations in which a section of DNA is lost, or deleted.
Primer designs are shown for site-directed mutation (A), deletion (B) and insertion (C). Triangles, DEL and INS indicate the locations of the mutations, deletion and insertion respectively in the primer sequences. These mutations are often considered more harmful than substitutions, because they impact upon the way the rest of the sequence is read by the cell.
F508del: deletion of phenylalanine (F) in 5: Duplication : c. G4_Q6dup: duplication of the segment from glycine (G) in to glutamine (Q) in : Insertion : c. The severity of the condition and the signs and symptoms depend on the size and location of the deletion and which genes are involved. The process of spontaneously occurring deletion must include two chromosome breaks to cut out the intervening segment.

If the two ends join and one of them bears the centromere, a shortened chromosome, which is said to carry a deletion. Mutations can also influence the phenotype of an organism.
Chromosome Mutations – I. This tutorial looks at the effects of chromosomal mutations, such as nondisjunction, deletion, and duplication. Deletion mutation is deletion of a base from the genetic sequence, which changes the codon reading frame beyond the point of mutation.
Substitution mutation involves replacement of a base (e.g. one purine) by another base (either purine or pyrimidine). Insertion or deletionin a frame-shift that changes the reading of subsequent codons an therefore, alters the entire amino acid sequence that follows the mutation, insertions and. An Efficient One-Step Site-Directed Deletion, Insertion, Single and Multiple-Site Plasmid Mutagenesis Protocol BMC Biotechnol.
Material, such as a word or passage, that has been removed from a body of written or printed matter. Genetics The loss, as through mutation, of one or more nucleotides from a chromosome. Scientists have found more than 7different mutations in the CFTR gene that can cause CF. Substitution Mutation Definition A substitution mutation is a type of replication error during DNA replication which places the wrong nucleotide or sequence of nucleotides in the wrong position.
A type of substitution mutation, a point mutation, occurs which a single nucleotide is substituted. This can be seen in the image below.
Hiç yorum yok:
Yorum Gönder
Not: Yalnızca bu blogun üyesi yorum gönderebilir.